We all know individuals who have been able to use marijuana and be happy, successful and productive members of society. The precise proportion of users who fall into this category is not known, but what is clear is a substantial percentage of people cannot use marijuana with impunity. Unfortunately, you can’t tell ahead of time who that is going to be. There is no genetic test, no psychological profile, no family history screening that is reliable.
The question becomes not how many fatalities does use of marijuana cause, but can a young person use it occasionally, i.e. “responsibly,” like having a single beer once a month or once a week, and be sure that they’ll be O.K.? The answer is no, particularly in regards to psychotic outcomes. Some individuals experience acute psychosis after their first use.
1) Psychosis: hundreds of peer-reviewed, scientific articles show a correlation between marijuana use and psychotic outcomes such as schizophrenia, too numerous to list here. The question of whether marijuana is causal for psychosis has been answered in the affirmative by applying standard principles of causation used in pharmacological and epidemiological research:
- Dose response effect, so that heavier use of more potent product results in more users developing schizophrenia(Zammit et al., 2002; van Os et al., 2002; DiForti et al., 2009; DiForti et al., 2015)
- Administration of the active ingredient (∆9-THC) in the clinic under controlled conditions causes psychotic symptoms (D’Souza et al., 2004; Morrison et al., 2011; Bhattacharyya et al., 2011; Freeman et al., 2014).
- Self-medicating is not that likely, because many will try to quit to avoid the psychotic symptoms before they become too impaired (Fergusson et al., 2005), e.g. comedian Seth McFarlane; but for others it may be too late (as seen in The Other Side of Cannabis, Heartsgate Productions, 2015).
- Marijuana use generally comes before the psychosis, not vice-versa (Arseneault et al., 2002; Henquet et al., 2005; Kuepper et al., 2011).
- In users who have schizophrenia, the age of onset is earlier than for non-users, similar to the effect of carcinogens in causing an earlier onset of a suite of cancers (Veen et al., 2004; Barnes et al., 2006; Large et al., 2011)
- Of all recreational drugs, marijuana use is the most likely to result in chronic psychosis (Niemi-Pynttari et al., 2013).
What percentage experience a psychotic outcome? The low to moderate-strength marijuana available in the last century was shown to trigger single psychotic symptoms (paranoia, racing thoughts, delusions, hallucinations) in 12% to 15% of users (Thomas, 1996; Barkus et al., 2006; Smith et al., 2009). Of those with such “prodromal” symptoms, about 35% can be expected to develop full psychosis, i.e. a constellation of symptoms occurring at once (Cannon et al., 2008). For about half of these individuals, conversion to chronic schizophrenia spectrum disorder occurs irrespective of family history (Arendt et al., 2008; Niemi-Pynttari et al., 2013).
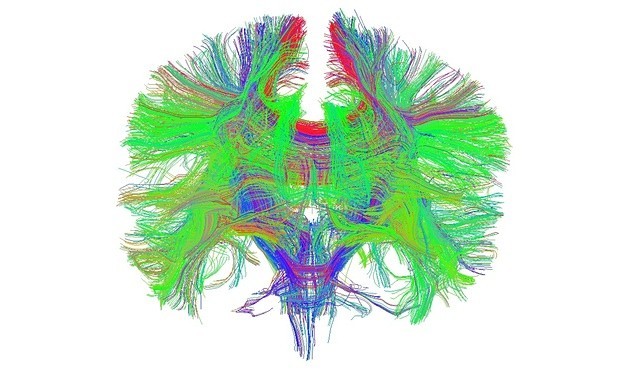
The result for low to moderate-strength marijuana was about a 2.5-fold increased risk of schizophrenia, but for the high strength product available today, the risk for schizophrenia is 5-fold compared to non-users (DiForti et al., 2015). That increase in risk translates into about one out of every twenty users if they don’t quit in time. Is this impact limited to adolescence? Given that the brain continues to develop in males through the late twenties (see figure on back), it seems unlikely that the risk for chronic psychosis is limited to adolescent users. Furthermore, administration of THC to adults in a clinical setting results in psychotic symptoms (D’Souza et al., 2004; Morrison et al., 2011. Bhattacharyya et al., 2011; Freeman et al., 2014).
Other Adverse Psychological Outcomes
2) Risks for anxiety, panic, and depression are increased by marijuana use: Zuardi et al., 1982; Thomas, 1996; Patton et al., 2002; Dannon et al., 2004; Hayatbakhsh et al., 2007; Medina et al., 2007; Hasin et al., 2008; Zvolensky et al., 2010; Fairman and Anthony, 2012; Silins et al., 2014; Cougle et al., 2015; with some studies showing that correction for confounding variables lessens the association with anxiety and depression, while others report the effect remains. For a review see: Miller CL, The Impact of Marijuana on Mental Health in: Contemporary Health Issues on Marijuana (Winters KC and Sabet K, eds), Oxford University Press, in press.
3) Risk for suicidal ideation is increased on average 7-fold: Arendt et al., 2006; Silins et al., 2014; Kvitland et al., 2016 , even after correcting for a prior history of depression: Clarke et al., 2014. In 2014 (the report specific for 2015 data is not yet available), the 2nd year after legalization of recreational use of marijuana, Colorado experienced the highest suicide rate in state history: “In 2014, there were 1,058 suicides among Colorado residents and the age-adjusted suicide rate was 19.4 per 100,000. This is the highest number of suicide deaths ever recorded in Colorado.” Office of Suicide Prevention Annual Report 2014-2015, Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment.
Particularly alarming, the Colorado media has reported sudden onset suicidal ideation or completed suicide in consumers of commercial edibles: Levi Thamba Pongi, Denver, 2014; Richard Kirk, Denver, 2014; Luke Goodman, Keystone, 2015, but also reported following the smoking of potent marijuana: Brant Clark, Boulder, 2007; Daniel Juarez, Brighton, 2012. (Editor’s note: In Seattle, 16-year-old Hamza Warsame jumped six floors to his death after smoking marijuana in December, 2015.) These responses can happen so quickly in individuals who were not previously suicidal that intervention may be impossible.
4) Lack of educational achievement and decreases in motivation – after covariate adjustment, the odds for marijuana users completing high school are reduced to about 0.37-fold that of controls (Silins et al., 2014); accounting for demographics and other factors, marijuana use adversely affected college academic outcomes, both directly and indirectly through poorer class attendance (Arria et al., 2015); decreases in motivation with marijuana use have been documented in clinical studies of humans (Bloomfield et al., 2014) and in animal models (Silveira et al., 2016).
5) Negative impacts on IQ: up to an approx. 7 point drop in IQ from childhood scores by age 38 in marijuana users who have been abstinent for 24 hours prior to testing; but only an approx. 5 point drop in those abstinent for a week prior to testing (Meier MH et al., 2012); a subsequent study of twins by Jackson et al., 2016, yielded mixed results, with an average decline of 4 points in marijuana users by late adolescence, however restricting the comparison to the matched twins (thereby controlling for genetics and a myriad of environmental factors), the effect of marijuana largely disappeared. The limitation of this later study is that brain development is not complete by late adolescence, particularly the wiring of the all-important cortex is still ongoing through the late twenties (see Figure below). There is no controversy, however, about the negative, real-time impact of marijuana use during tests of cognition and memory: Curran HV et al., 2002; Ranganathan and D’Souza, 2006; Morrison et al., 2009; Solowj et al., 2010; Pavisian et al., 2014.
By Christine Miller, Ph.D., for Moms Strong. Dr. Miller also wrote Ten Myths Marijuana Advocates Want You to Believe.
See 10 Myths Marijuana Advocates Want You to Believe for complete information, footnotes and the bibliography