by SAM (Smart Approaches to Marijuana) Smart Approaches to Marijuana’s 2017 publication references academic studies which suggest that marijuana primes the brain for other types of drug usage. Here’s the summary on that subject from page 4, Marijuana and Other Drugs: A Link We Can’t Ignore :
MORE THAN FOUR in 10 people who ever use marijuana will go on to use other illicit drugs, per a large, nationally representative sample of U.S. adults.(1) The CDC also says that marijuana users are three times more likely to become addicted to heroin.(2)
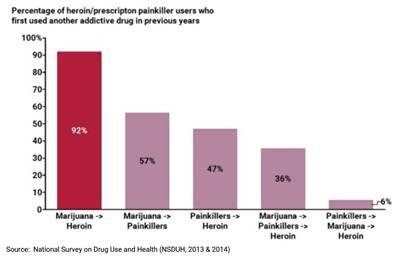
And according to the seminal 2017 National Academy of Sciences report, “There is moderate evidence of a statistical association between cannabis use and the development of substance dependence and/or a substance abuse disorder for substances including alcohol, tobacco, and other illicit drugs.”(3)
RECENT STUDIES WITH animals also indicate that marijuana use is connected to use and abuse of other drugs. A 2007 Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology study found that rats given THC later self administered heroin as adults, and increased their heroin usage, while those rats that had not been treated with THC maintained a steady level of heroin intake.(4) Another 2014 study found that adolescent THC exposure in rats seemed to change the rodents’ brains, as they subsequently displayed “heroin-seeking” behavior. Youth marijuana use could thus lead to “increased vulnerability to drug relapse in adulthood.”(5)
National Institutes of Health Report
The National Institutes of Health says that research in this area is “consistent with animal experiments showing THC’s ability to ‘prime’ the brain for enhanced responses to other drugs. For example, rats previously administered THC show heightened behavioral response not only when further exposed to THC, but also when exposed to other drugs such as morphine—a phenomenon called cross-sensitization.”(6)

ADDITIONALLY, THE MAJORITY of studies find that marijuana users are often polysubstance users, despite a few studies finding limited evidence that some people substitute marijuana for opiate medication. That is, people generally do not substitute marijuana for other drugs. Indeed, the National Academy of Sciences report found that “with regard to opioids, cannabis use predicted continued opioid prescriptions 1 year after injury. Finally, cannabis use was associated with reduced odds of achieving abstinence from alcohol, cocaine, or polysubstance use after inpatient hospitalization and treatment for substance use disorders” [emphasis added].(7)
Moreover, a three-year 2016 study of adults also found that marijuana compounds problems with alcohol. Those who reported marijuana use during the first wave of the survey were more likely than adults who did not use marijuana to develop an alcohol use disorder within three years.(8) Similarly, alcohol consumption in Colorado has increased slightly since legalization. (9)
Data on Marijuana Policy for 2017
Here’s the complete Data on Marijuana Policy for 2017 in pdf form.
FOOTNOTES:
- Secades-Villa R, Garcia-Rodríguez O, Jin CJ, Wang S, Blanco C Probability and predictors of the cannabis gateway effect: a national study. Int J Drug Policy. 2015;26(2):135-142
2. Centers for Disease Control. Today’s heroin epidemic Infographics more people at risk, multiple drugs abused. CDC, 7 July 2015.
3. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Board on Population Health andPublic Health Practice; Committee on the Health Effects of Marijuana: An Evidence Review and Research Agenda (“2017 NAS Report”).
4. Ellgren, Maria et al. “Adolescent Cannabis Exposure Alters Opiate Intake and Opioid Limbic Neuronal Populations in Adult Rats.”Neuropsychopharmacology 32.3 (2006): 607–615.
5. Stropponi, Serena et al. Chronic THC during adolescence increases the vulnerability to stress-induced relapse to heroin seeking in adult rats. European Neuropsychopharmacology Volume 24 , Issue 7 (2014), 1037 – 1045.
6. “Is marijuana a gateway drug?” National Institute on Drug Abuse. Jan. 2017. See also Panlilio LV, Zanettini C, Barnes C, Solinas M, Goldberg SR. Prior exposure to THC increases the addictive effects of nicotine in rats. Neuropsychopharmacol Off Publ Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013;38(7):1198-1208; Cadoni C, Pisanu A, Solinas M, Acquas E, Di Chiara G. Behavioural sensitization after repeated exposure to Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cross-sensitization with morphine. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2001;158(3):259-266.
7. 2017 NAS report.
8. Weinberger AH, Platt J, Goodwin RD. Is cannabis use associated with an increased risk of onset and persistence of alcohol use disorders? A three-year prospective study among adults in the United States. Drug Alcohol Depend. February 2016.
This is the second recent article on the gateway effects of marijuana use. Since marijuana has already primed the brains of most people who get addicted to opioids, marijuana cannot replace pain pills.



