Smart Approaches to Marijuana released its latest report in September 2020. From the various graphs, data and statistics, it is clear that the harmful consequences of marijuana use are more extreme in states that have legalized marijuana. State regulation fails in a number of ways highlighted in the report:
- In legal pot states, youth use at higher rates and they “dab” at higher rates than the states without a marijuana industry. There’s a 25% increase in youths with Cannabis Use Disorder in states that legalized pot. The increase follows the increase in marijuana potency, as pot shops sell the most addictive products that create the highest demand. Between 30-40% of teen pot users in Oregon and Colorado report dabbing; dabs have upwards of 50% THC content.
- At least 18% of traffic fatalities in Colorado and Washington involve drivers impaired by THC. Driving under the influence of THC remains a huge problem, as pot users believe they aren’t impaired.
An increasingly stoned driving population poses a problem to law enforcement officers who attempt to stop and detain marijuana-impaired drivers. Some states no longer allow the smell of marijuana in a driver’s car as a reason to make a search or arrest, even in states where marijuana is illegal. Technology to determine lacks the accuracy of traditional breathalyzers used to test alcohol impairment. Recently, scientists found that drivers may still be impaired from marijuana use well after intoxication. Many of the marijuana “legal” states failed to establish laws or guidance prior to legalizing marijuana.
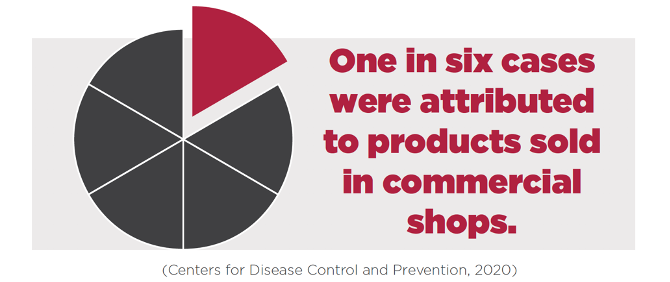
Although the marijuana industry attributed the vaping illnesses exclusively to black market vapes, some of the tainted vapes came from state-regulated pot shops - One sixth of the reported vaping illnesses came from vapes purchased at state-regulated marijuana dispensaries. These tainted vapes included those purchased for both “medical” and “recreational” purposes. Amongst those who became sick from vaping, 82% vaped THC. The marijuana industry has not proven to be capable of allowing regulation.
- Polydrug use is a growing problem. Many recent studies show that marijuana use increases the use of alcohol, opioids and tobacco.
- In states with legalized pot, there are higher rates of all substance use disorders.
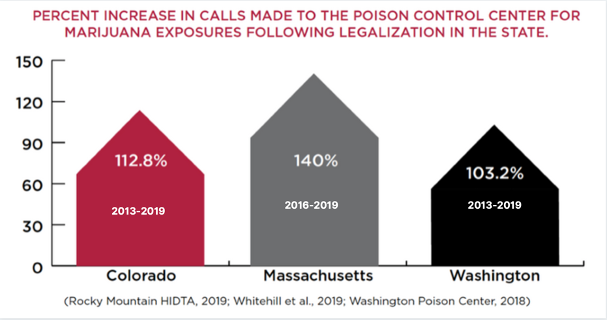
- More marijuana-related emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and accidental exposures.
- Expansive Increases in workplace problems, including labors shortages and accidents.
- Increase in homelessness, including people who move to the states for easy access to marijuana.
- Increases in crime and lucrative criminal markets. Huge arrests of international cartels, from many countries in Asia, Europe and Latin America, demonstrate how the legal pot market invites criminal activity. These drug sellers move into states with legalization, where they can buy up property, grow indoors or outdoors, and hide behind the legal market.
- Exacerbated racial disparities in marijuana industry participation and criminal justice enforcement. Since marijuana was sold to the public as a social justice issue, it’s disturbing to learn that most dispensaries are owned primarily by whites. States trying to create a social equity component to their legalization find it impossible, as is currently happening in Illinois.
Many big players in the tobacco, pharmaceutical and alcohol industries are buying major stakes in marijuana, hoping to monopolize the industry. These players contribute heavily to politicians and state legalization campaigns.
SAM is a leading educational anti-marijuana organization in the United States. It emphasizes the middle ground between legalization and incarceration, and it also shows how legalization with commercialization fails.